What is block chain?
Blockchain is a decentralized ledger for all transactions over a peer-to-peer network. This technology allows participants to confirm transactions without the need for a central accounting authority.
The blockchain is an immutable (unchangeable, meaning a transaction or file recorded cannot be changed) distributed digital ledger (digital record of transactions or data stored in multiple places on a computer network) with many use cases beyond cryptocurrencies.
Why Blockchain technology has so much of importance
With the advent of technology, businesses are more data driven and information belongs to it is very imperative. The faster and more accurate the reception, the better. Blockchain is ideal for delivering that information because it provides instantly shared, fully transparent information stored in an immutable ledger that is accessible only to authorized network members. The blockchain network can track orders, payments, invoices, production and more. Members also share a single view of the truth, giving them end-to-end access to all the details of the transaction, increasing confidence and gaining new efficiencies and opportunities.
Fundamental elements of block chain
- Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) refers to a technology infrastructure and protocol that enables simultaneous access, validation, and updating of immutable records across a network that spans multiple entities or locations.
Well-known as blockchain technology, DLT was introduced by Bitcoin and is now a buzzword in the technology world given its industry and sector-wide potential. Simply put, DLT is about the concept of a “distributed” network as opposed to a traditional “centralized” mechanism, which is seen as a widespread impact on industries and entities that have long relied on trusted third parties.
Fig. Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
- Immutable records
Immutability can be defined as the ability to keep the blockchain ledger unchanged and the blockchain to remain unchanged. More simply, the data on the blockchain cannot be modified.
Each block of information, such as facts and transaction details, proceeds using cryptographic principles or hash values. Its hash value consists of an alphanumeric string generated individually by each block. Each block contains the signature of the previous block as well as its own hash or digital signature. This connects the blocks retroactively and relentlessly. This feature of blockchain technology prevents anyone from breaking into the system or modifying the data stored in the block.
It is also important to know that blockchain is inherently decentralized and decentralized, creating consensus among the various nodes that store data replication. This consensus requires us to maintain the originality of our data. Undoubtedly, immutability is a hallmark of this technology. This concept has the ability to redefine the entire data auditing process, making it more efficient and cost-effective, and improving the reliability and integrity of your data.

Fig. Immutable records
- Smart contract
A smart contract is a self-executing contract in which the terms and conditions of the contract between the buyer and the seller are described directly in the rule code. The code and the similarities it contains consist of decentralized and decentralized blockchain networks. The code controls execution and transactions are traceable and irreversible.
Smart contracts enable you to carry out reliable transactions and agreements between diverse and anonymous parties without the need for central authorities, legal systems, or external compliance mechanisms.
Blockchain technology is primarily considered the foundation of Bitcoin, but has evolved far beyond the support of cryptocurrencies.
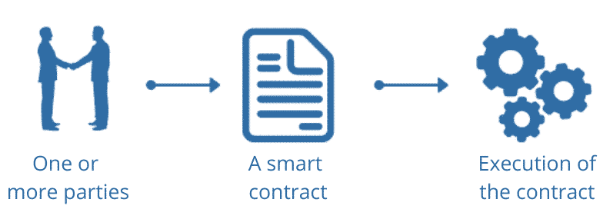
Fig. Smart contract
How it’s beneficial
Blockchain solutions are not limited to cryptocurrency exchanges. Because this technology is decentralized and decentralized, it has many advantages that can be offered to companies in different industries.
- Greater Transparency
The most important feature of blockchain is the fact that transaction ledgers with public addresses can be viewed. The business and financial systems add an unprecedented level of responsibility, placing all sectors of the business responsible for acting in good faith in the growth of the enterprise, its community, and its customers.
- Increased Efficiency
Because blockchain is decentralized, many processes in areas such as payments and real estate do not require an intermediary. Compared to traditional financial services, blockchain facilitates faster transactions by enabling P2P cross-border transfers in digital currencies. The real estate management process is made more efficient by an integrated system of real estate records and smart contracts that automates tenant-landlord agreements.
- Better Security
The blockchain is much more secure than other records management systems because the new transaction is encrypted and linked to the previous transaction. As the name implies, a blockchain consists of a network of computers gathered to identify a “block”, and this block is added to the ledger that forms the “chain”. A blockchain is made up of a complex chain of mathematical numbers that cannot be changed once formed. This immutable and immortal nature of the blockchain protects it from counterfeit information and hackers. Its decentralized nature also gives it a unique “trustless” quality.
- Improved Traceability
With the blockchain ledger, every time a product exchange is recorded on the blockchain, an audit trail is presented to track where the product is coming from. It not only improves the security of exchange-related businesses and prevents fraud, but also helps verify the authenticity of traded assets. In industries such as medicine, it can be used to track the supply chain from manufacturer to distributor. It can also be used in the arts industry to provide irrefutable proof of ownership.
How transaction happens?
- As every transaction initiated, it is recorded as a “block” of data
These transactions show the movement of assets that may be tangible (product) or intangible (intellectual). Data blocks can record selected information such as who, what, when, where, how much, and even conditions.
- Each block is interlinked in chain form, connected to the ones before and after it
These blocks form a chain of data when an asset moves from one place to another or changes ownership of its owner. The blocks are securely linked to ensure the exact time and order of transactions and to prevent the blocks from being tampered with or inserted between two existing blocks.
- Unidirectional flow of block linked in a chain-Transactions are blocked together in an irreversible chain: a blockchain
Each additional block enhances the validation of the previous block and thus the entire chain of blocks. This makes the blockchain self-evident and provides an important force of immutability. This prevents malicious attackers from being tampered with and creates a record of transactions that you and other members of your network can trust.

Fig. Blockchain transaction
Blockchain network types
- Public blockchain networks
A public blockchain is one that anyone can join and participate in, such as Bitcoin. Disadvantages may require considerable computing power, such as little or no transaction privacy or inadequate security. These are important considerations for blockchain business use cases.
- Private blockchain networks
Private blockchain networks, like public blockchain networks, are decentralized peer-to-peer networks. However, one organization controls the network, controls who can join, manages consensus protocols, and maintains a shared ledger. Depending on the use case, trust among participants can be significantly increased. Private blockchains can be managed behind corporate firewalls and can even be hosted on-premises.
- Permissioned blockchain networks
Enterprises that set up a private blockchain usually set up a permissioned blockchain network. It is important to note that public blockchain networks may also have permissions. This limits the network and the users who can participate in a particular transaction. Participants must receive an invitation or permission to participate.
- Consortium blockchains
Multiple organizations can share the responsibility of maintaining the blockchain. These finalists will determine who can send transactions and access data. Consortium blockchain is ideal for businesses where all participants need blockchain permission and shared responsibility.

